About Me
I am a Ph.D. student in Computer Science at the University of Missouri, advised by Dr. Tanu Malik. My research focuses on Efficiency in LLMs, Trustworthy AI, and Reproducibility in Systems. In Summer 2026, I will join Microsoft as a Research Data Science Intern.
Previously, I completed my M.S. in Computer Science at Missouri, advised by Dr. Jianlin Cheng and Dr. Grant Scott. I received my B.Tech from VIT University (Vellore Institute of Technology), where I worked on multilingual sentiment analysis advised by Dr. Soughbhagya Barpanda, with dataset and collaboration support from Dr. P. Kumaraguru (PRECOG, IIIT Hyderabad).
I was selected as a Google PhD Fellowship Nominee (2025) in NLP, one of three nominees from Missouri, and received the Outstanding Master’s Student Award (2025).
Research Interests: LLMs, NLP, Agentic AI, Trustworthy AI, Scalable ML Systems, Reproducibility
News
- 2025.12: Two papers accepted at AAAI 2026
- 2025.11: Joining Microsoft as Research Data Science Intern (Summer 2026)
- 2025.05: Earned my M.S. in Computer Science (GPA: 4.0/4.0) from the University of Missouri
- 2025.05: Received the Outstanding Master’s Student Award from the MU College of Engineering
- 2025.04: Selected as a Google PhD Fellowship Nominee (NLP) — one of three nominees from Missouri
- 2025.03: Achieved Runner-Up in the MUIDSI AI Hackathon ($1,000 prize)
- 2025.01: Two papers accepted at AAAI 2025
- 2024.01: Working as a TA for 100+ students in Web Development
- 2023.08: Began Ph.D. research on faithfulness, interpretability, and robustness in LLMs
- 2023.05: Graduated with B.Tech from VIT Vellore
Publications
2026

2025

Thesis & Earlier Work




Honors and Awards
Education
Ph.D. in Computer Science, University of Missouri
Advisor: Dr. Tanu Malik | GPA: 3.9/4.0
Research: Trustworthy AI, LLM Efficiency, Reproducibility
Funded by NASA, NSF, and Department of Defense
M.S. in Computer Science, University of Missouri
Advisors: Dr. Jianlin Cheng, Dr. Grant Scott | GPA: 4.0/4.0
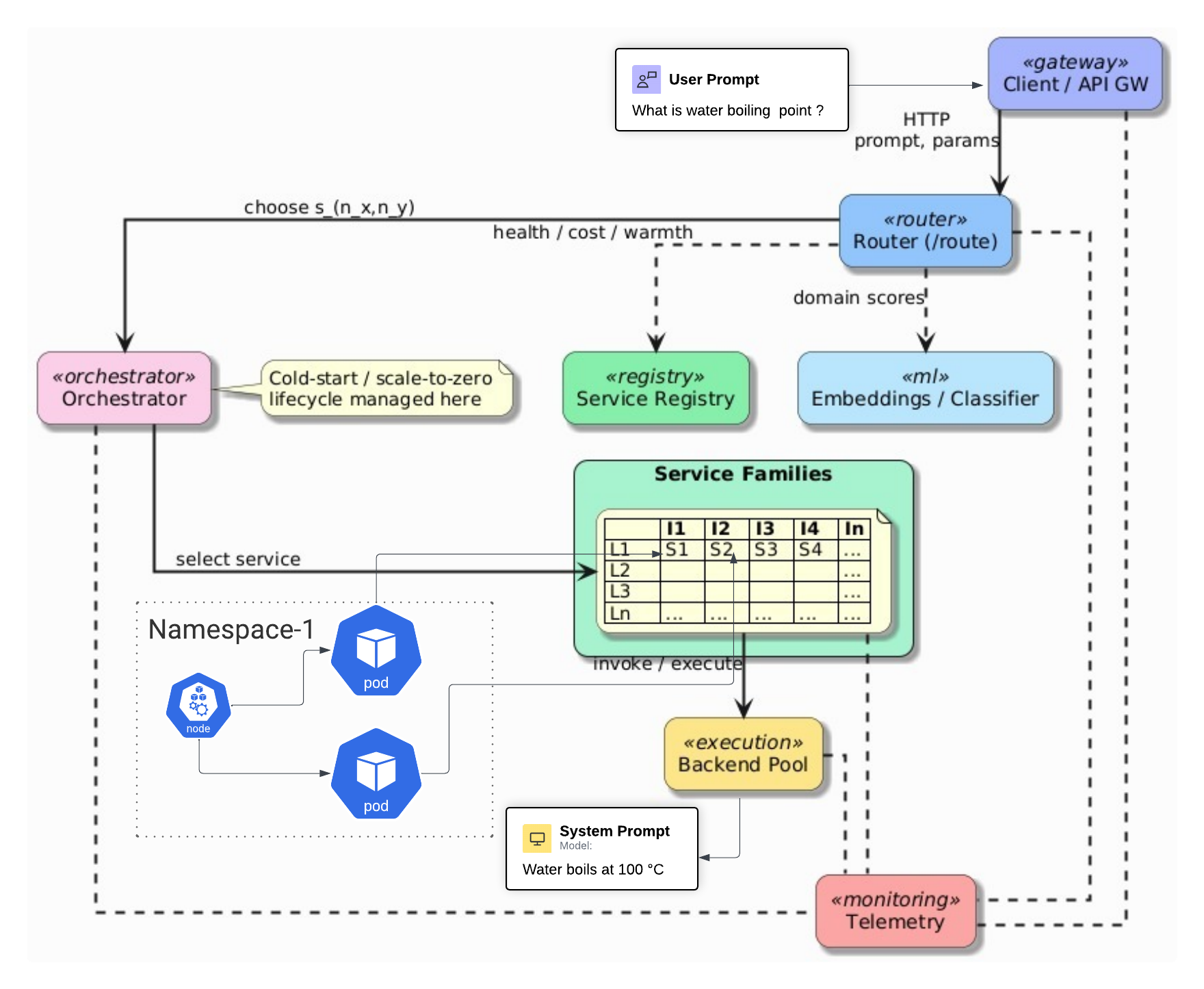
Thesis: Deploying LLM-as-a-Service in Kubernetes HPC Clusters
B.Tech in Computer Science (Data Analytics), VIT Vellore
Thesis: Multilingual Sentiment Analysis on KOO platform
Awards: Dean's Research Excellence Award, Best Thesis Award
Experience
Microsoft — Research Data Science Intern
University of Missouri, Radiant Lab — Research Assistant
NASA-funded research on reproducible scientific containers and self-reflecting LLMs
Advisor: Dr. Tanu Malik
University of Missouri, Data Intensive Computing Lab — Research & Teaching Assistant
DoD/NSF-funded research on hallucination detection in LLMs (30% improvement)
TA for Web Development: mentored 115+ students
Advisors: Dr. Grant Scott, Dr. Jianlin Cheng
Adobe — Volunteer Research Intern
Web scraping and information extraction for NLP team
Service
Reviewer: NeurIPS, ICML, ACL, CVPR, ICLR, AAAI, EMNLP, ECCV, ICCV, IJCAI, NAACL, ICASSP
Journals: TPAMI, TIP, TMLR, JVCI
Teaching
- Teaching Assistant, Web Development (MERN Stack) — Fall 2025, Fall 2024, Spring 2024, Fall 2023





